Manufactured Wood, also known as engineered wood, is a concept that is no longer strange in the modern construction and interior design industry. This is a type of material created from the combination of wood particles, wood fibers or plywood with adhesives using high technology, to create a high-application and sustainable alternative material. To go deeper into the concept of what manufactured Wood is and the popular types of industrial wood today, let’s find out together in the article below.

Table of Contents
What is Manufactured Wood?
What is Manufactured Wood? This is a question that has been of great interest to many people, especially in the context of increasingly depleted natural wood resources and rising prices.
Manufactured Wood, also known as industrial wood, refers to a wide range of composite wood products that are widely used in construction and furniture making. These products include plywood, particleboard, MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard), OSB (Oriented Strand Board), and many others, which are created through the process of pressing wood fibers, chips, or panels together with adhesives to form a new material with superior properties compared to natural wood.
Based on the components used and the construction projects for which they are intended, Manufactured Wood is produced in various types, such as plywood, fiberboard, particleboard, etc.

Different Types of Manufactured Wood
Once you have a better understanding of what manufactured wood is, it is also important to classify the different types. There are many types of manufactured wood commonly used today. Each different type of industrial wood will be produced using different materials to suit each user’s purpose.
Plywood
Plywood is one of the most popular types of manufactured wood in the world. It is also known for being the most sturdily manufactured wood. Plywood is made from multiple layers of thin veneers glued together to form a strong panel.
Depending on the number and quality of veneer layers used, plywood can be classified into different grades, A, B, C, D. Among these, grade A is the highest quality, often having durability and strength even exceeding that of solid wood. Accordingly, plywood is commonly used for everything from flooring and furniture to construction of structures, roofing, partitions, wall panels, etc.
- Advantages: The most outstanding advantage of plywood is its natural wood grain that looks like real wood. It has good water and compression resistance, is also highly workable and has the ability to resist attack from termites and insects. Plywood is also very easy to machine, glue, paint and polish.
- Disadvantages: While there are many moisture-resistant types, not all plywood is suitable for outdoor use. In addition, the quality of plywood depends largely on the quality of the veneer and adhesive used. It is also one of the most expensive types of industrial wood to produce.
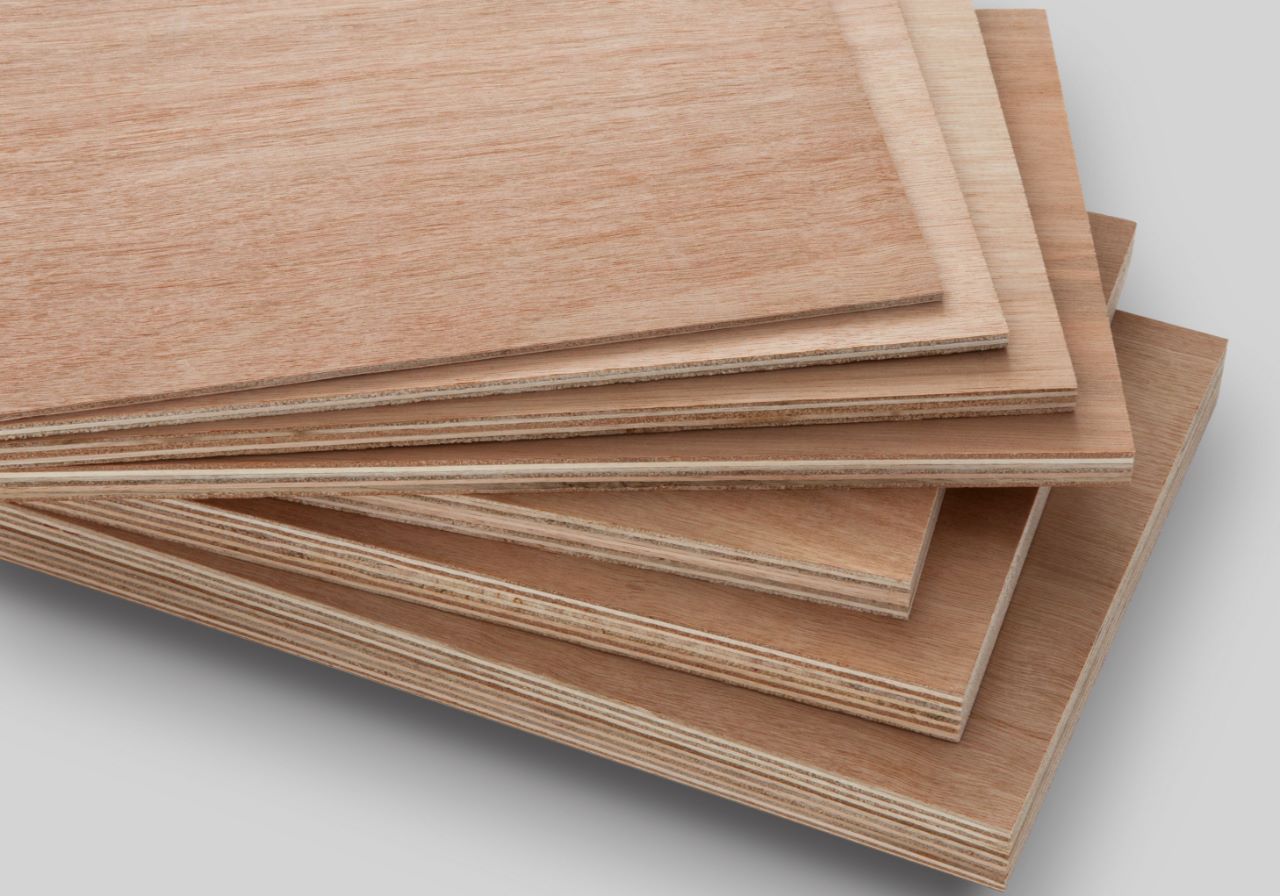

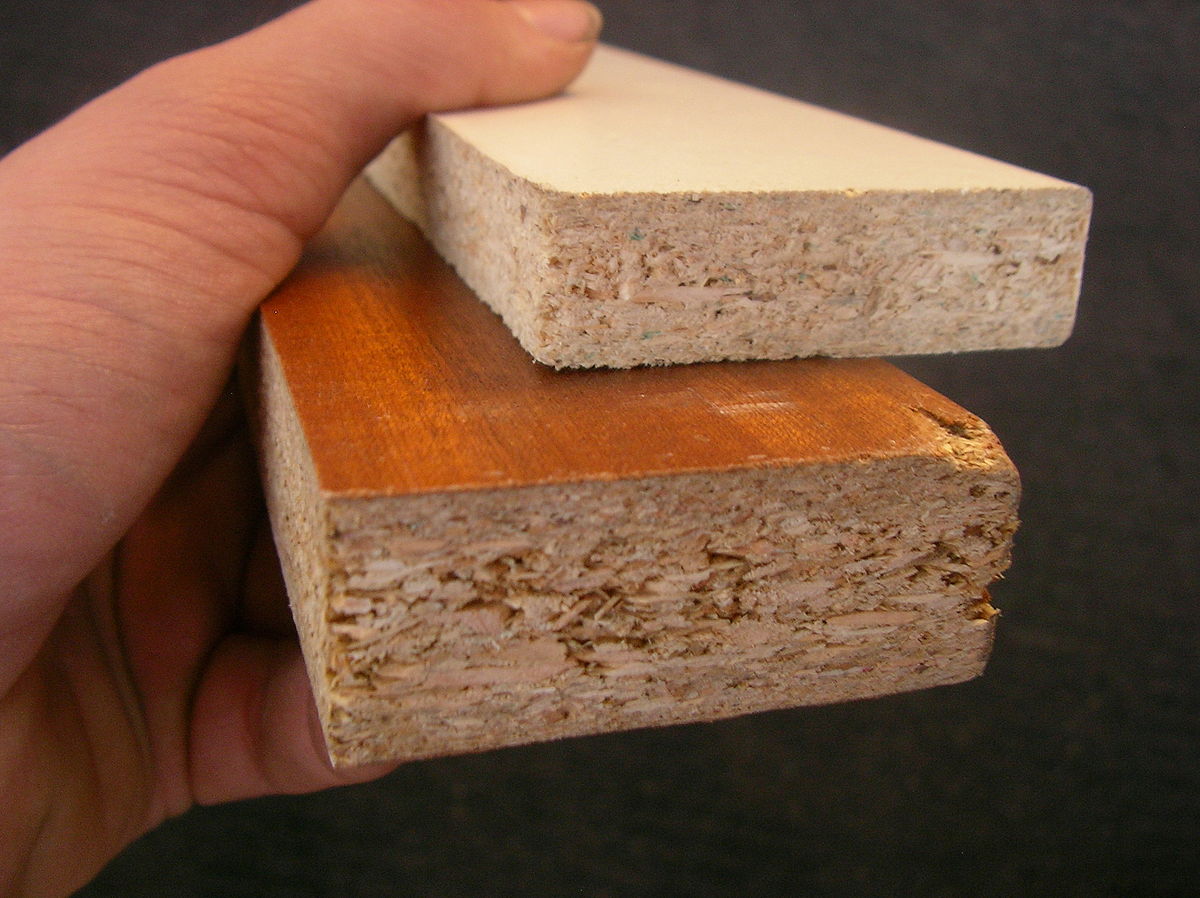
Particleboard or Chipboard
Particleboard is one of the most affordable types of manufactured wood, produced by combining sawdust, resin, and adhesives to form a hard panel. Particleboard is often used as a substitute for solid wood or plywood in projects where cost optimization is prioritized over quality. With its low price, particleboard is widely used in construction projects and furniture manufacturing with limited budgets. To improve the appearance and durability, manufacturers often apply veneer layers to both sides of the particleboard, increasing the aesthetics and durability of the product.
Particleboard is commonly used in affordable furniture such as wall panels, partitions, flooring, suspended ceilings, and doors.
- Advantages: Particleboard is low-priced and readily available, making it a versatile industrial wood alternative and a suitable choice for low-end furniture production. Easy to maintain, it is also easy to paint and laminate.
- Disadvantages: Particleboard has lower durability compared to other types of industrial wood. It is less dense, has poor water resistance, and may release harmful chemicals, making it unsuitable for heavy load-bearing applications.

Fibreboard
Fiberboard, including MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard), is a material made from wood fibers that are crushed, mixed with adhesives, and pressed under high heat and pressure. Fiberboard is one of the strongest types of industrial wood, it is much denser than particleboard and has high abrasion resistance even with continuous use.
Depending on the quality of the material, fiberboard can be divided into the following types:
- MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard): This is a medium density fiberboard, it is durable and has better strength than low density fiberboard but less durable than HDF. MDF is suitable for outdoor projects due to its ability to withstand temperature and weather changes.
- LDF (Low Density Fiberboard): Low density fiberboard is similar to particleboard.
- HDF (High Density Fiberboard): High density fiberboard is similar to MDF but is more durable, harder and denser.

Fiberboard is very popular in furniture manufacturing, construction, soundproofing, and thermal insulation due to its easy cutting, drilling and painting.
- Advantages: It has a smooth, uniform surface with no voids, ideal for painting or wallpapering. It is also less expensive than plywood and environmentally friendly.
- Disadvantages: Fiberboard is not moisture resistant and is less durable than plywood. It can take longer to nail and install.
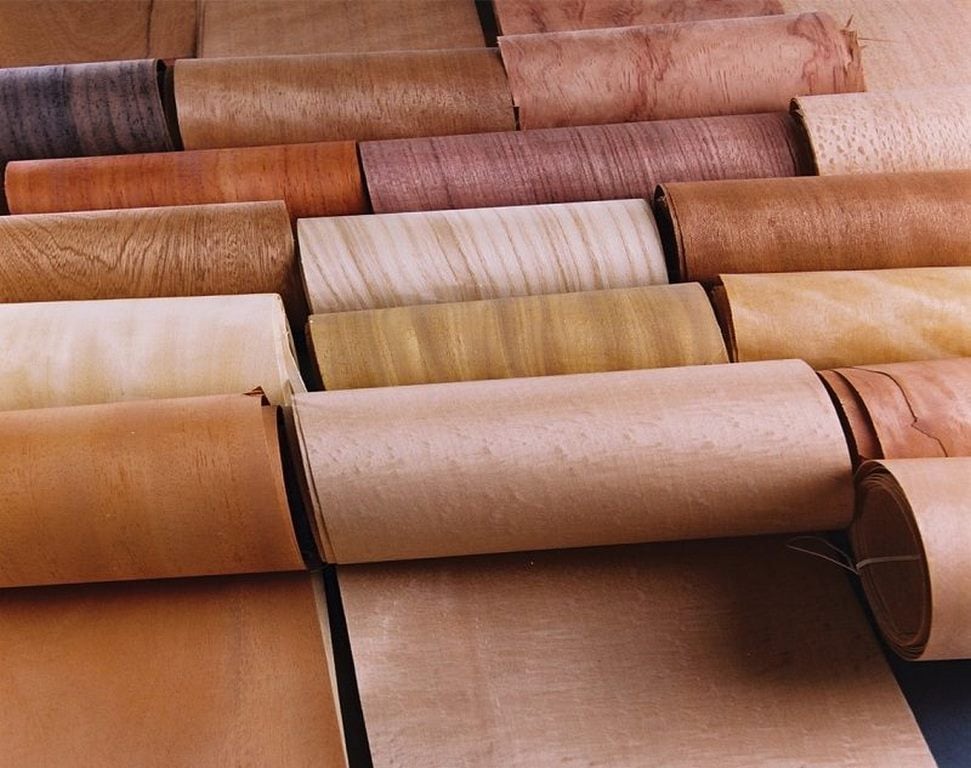
Veneer
Veneer is a thin layer of natural wood that is sliced and glued to the surface of engineered wood or other wood, often plywood, particleboard, or MDF (medium-density fiberboard). The main purpose of using veneer is to take advantage of the beauty of natural wood while still maintaining a lower cost than using solid natural wood.
Veneer is commonly used in furniture manufacturing, doors, or decorative panels. It is also used to make pianos, guitars, and other musical instruments to improve aesthetics without affecting the sound.
- Advantages: Veneer allows for the use of rare and expensive woods, creating a beautiful surface at a lower cost than using solid natural wood. Available in a variety of wood types, colors, and textures, veneer can be used to create a variety of styles and patterns.
- Disadvantages: As a thin layer, veneer is prone to scratches and damage if not handled carefully. Additionally, repairing scratches or damage to veneer can be more difficult than with solid natural wood due to the nature of the thin veneer layer.

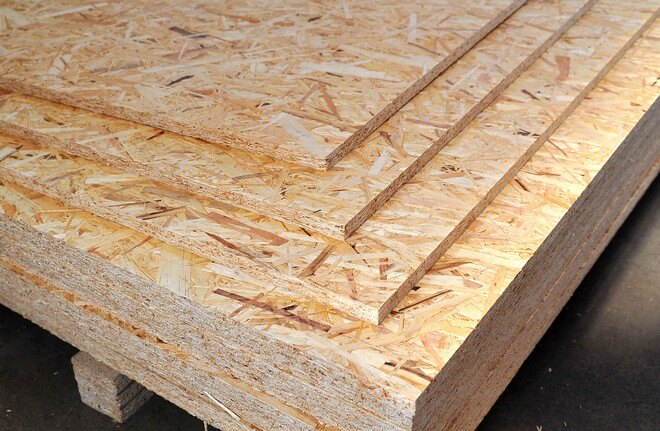
Oriented strand board (OSB)
Oriented Strand Board (OSB) is a type of engineered wood material made from carefully oriented wood strands (small strips of wood) bonded together with resin and adhesives. These wood strands are typically arranged in multiple layers, with each layer oriented in a different direction, creating a strong and uniform structure.
OSB is widely used in construction and is a staple material in wall framing, floor sheathing, furniture, packaging, and DIY projects.
- Advantages: OSB offers a more affordable price point compared to other types of plywood or solid wood. It also exhibits good strength and load-bearing capacity, making it suitable for construction, packaging, and furniture projects. Additionally, OSB is easy to work with, allowing it to be cut, shaped, and drilled using standard woodworking tools.
- Disadvantages: OSB is more prone to swelling and warping compared to plywood and solid wood, making it less suitable for use in humid environments. Moreover, OSB is not as durable as plywood, limiting its application in structural construction.

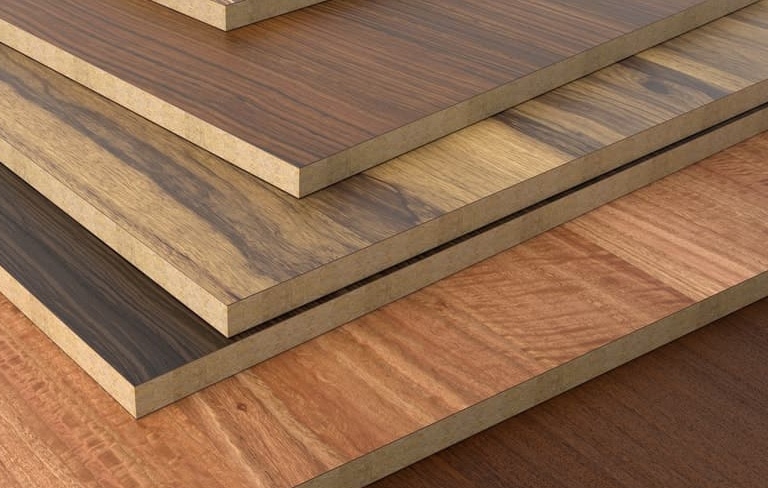
Blockboard
Blockboard is a type of engineered wood material, consisting of a core layer made from joined wooden slats and two outer faces covered with thin veneers or veneer. This structure creates a lightweight yet sturdy wood panel commonly used in furniture manufacturing and construction.
Blockboard’s lightweight and easy workability make it a suitable choice for DIY projects. It is also well-suited for finishing with paint, stain, or varnish to enhance its appearance.
- Advantages: Blockboard features a smooth texture, making it easy to finish with paint, stain, or varnish. Moreover, it is available in various thicknesses to accommodate different applications.
- Disadvantages: Blockboards may not be as durable as some other materials like plywood. It is also not suitable for outdoor projects or areas with high humidity.

Advantages and disadvantages of using manufactured wood
What makes industrial wood the most popular product with contractors today? Does it have any disadvantages that buyers need to pay attention to:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Manufactured wood is more affordable than solid wood, making it a financially sensible choice for many households. | Although sturdy in construction, manufactured wood is not as durable as solid wood and may not withstand heavy wear and tear. |
| Made from recycled wood fibers and other materials, it reduces the need for new wood and minimizes waste. | Excessive exposure to moisture can cause swelling, warping, and structural damage to manufactured wood products. |
| Can be easily shaped and molded into various forms, offering flexibility in furniture design and construction. | The lifespan of manufactured wood is generally shorter than that of solid wood, necessitating earlier replacement or repair. |
| Can be finished with various paints and stains, providing a wide range of aesthetic options to suit personal tastes. | Some types of manufactured wood may emit formaldehyde, a potentially harmful chemical that can affect indoor air quality. |
In conclusion, manufactured wood presents a viable alternative to solid wood, offering economic advantages and flexibility in use that make it particularly attractive for a wide range of applications. Its affordability and ability to utilize recycled materials contribute positively to environmental sustainability, reducing waste and the demand for new timber. Hopefully the above article has helped you understand more about industrial wood as well as the advantages and disadvantages it brings.







![[K-Timber] Blog Post Boder-3](https://k-timbers.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/K-Timber-Blog-Post-Boder-3.png)